Windows: SMB Enumeration
Introduction
Enumerating the SMB protocol is very important for pentesters. Before jumping into enumeration we should know what smb is.
SMB short for server message block is a protocol for sharing resources e.g (printers,files). It is commonly known to be found on port 445 or port 139. This protocol is available on windows by default.
Note: In Linux we must install a samba server because linux doesn't use the smb protocol.
Authentication should be set up e.g usernames and passwords and restrict which resources are shareable.
Security flaws:
- Using default credentials or not strong passwords. (Even no authentification in certain cases)
- Samba servers seem to be notorious for being insecure. A quick google search will reveal many exploits for smb. Patch it!
Checklist
- Enumerate Hostname -
nmblookup -A [ip]
List Shares
smbmap -H [ip/hostname]echo exit | smbclient -L \\\\[ip]nmap --script smb-enum-shares -p 139,445 [ip]
Check Null Sessions
smbmap -H [ip/hostname]rpcclient -U "" -N [ip]smbclient \\\\[ip]\\[share name]
Check for Vulnerabilities - nmap --script smb-vuln* -p 139,445 [ip]
Overall Scan - enum4linux -a [ip]
Manual Inspection
smbver.sh [IP] (port)[Samba]- check pcap
Tools
nmblookup- collects NetBIOS over TCP/IP client used to lookup NetBIOS names.smbclient- ftp-like client to access SMB sharesnmap- general scanner, with scriptsrpcclient- tool to execute client side MS-RPC functionsenum4linux- enumerates various smb functionswireshark
Enumerate Hostname
nmblookup
nmblookup -A [IP]
-A- look up by IP address
Example:

List Shares
smbmap
smbmap -H [ip/hostname]
This command will show you the shares on the host, as well as your access to them.
Example:
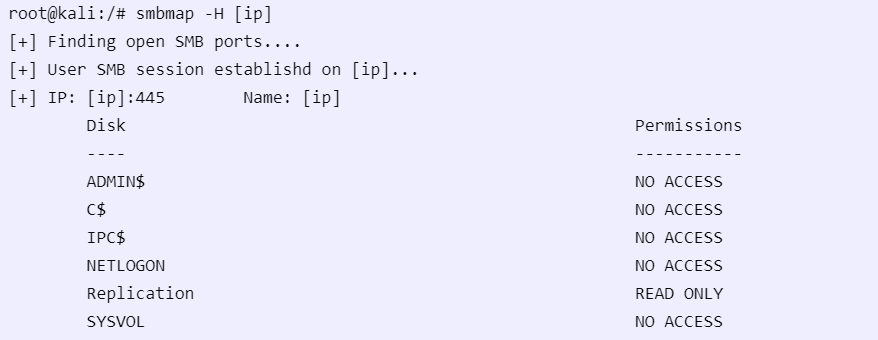
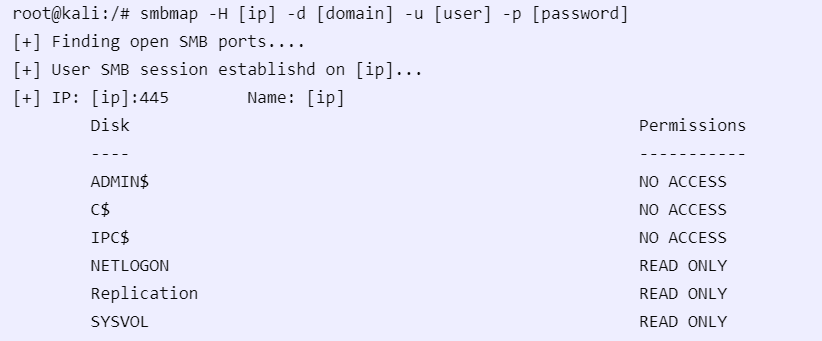
If you have credentials, you can re-run to show new access:
smbclient
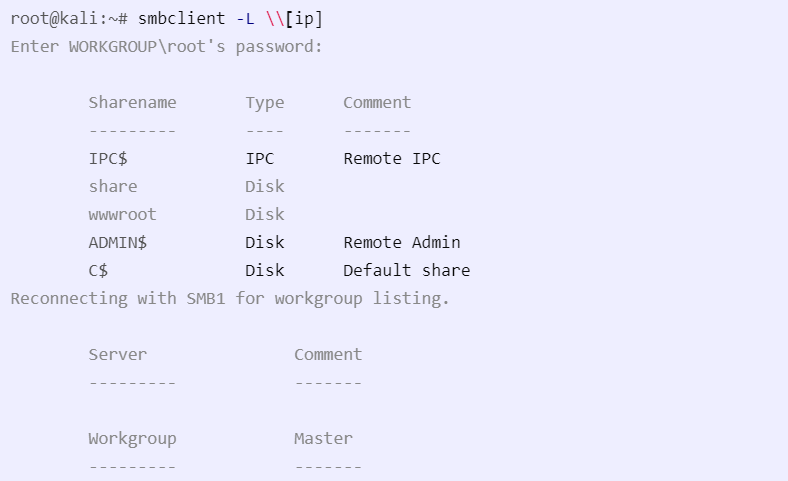
echo exit | smbclient -L \\\\[ip]
- exit takes care of any password request that might pop up, since we’re checking for null login
-L- get a list of shares for the given host
Example:
nmap
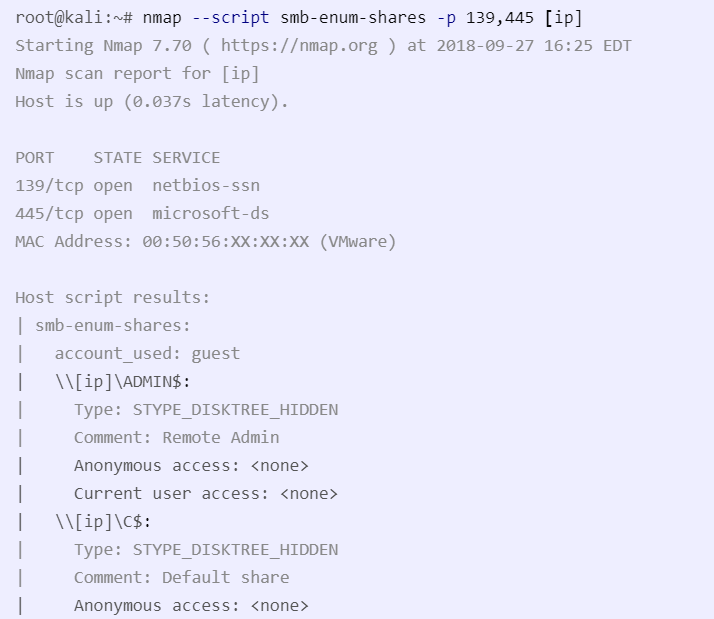
nmap --script smb-enum-shares -p 139,445 [ip]
--script smb-enum-shares- specific smb enumeration script-p 139,445- specify smb ports
Example:
Check Null Sessions
smbmap
smbmap -H [ip/hostname] will show what you can do with given credentials (or null session if no credentials). See examples in the previous section.
rpcclient
rpcclient -U "" -N [ip]
-U ""- null session-N- no password
Example:
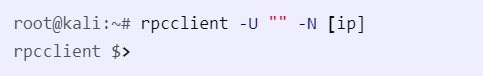
From there, you can run rpc commands.
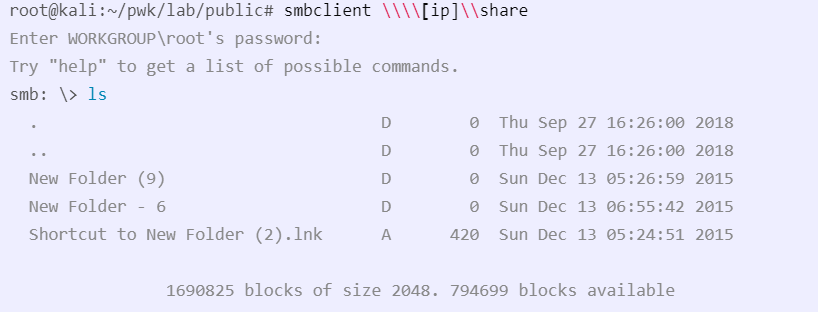
smbclient
smbclient \\\\[ip]\\[share name]
This will attempt to connect to the share. Can try without a password (or sending a blank password) and may be able to connect.
Example:
Check for Vulnerabilities
nmap
nmap --script smb-vuln* -p 139,445 [ip]
--script smb-vuln*- will run all smb vulnerability scan scripts-p 139,445- smb ports
Example:
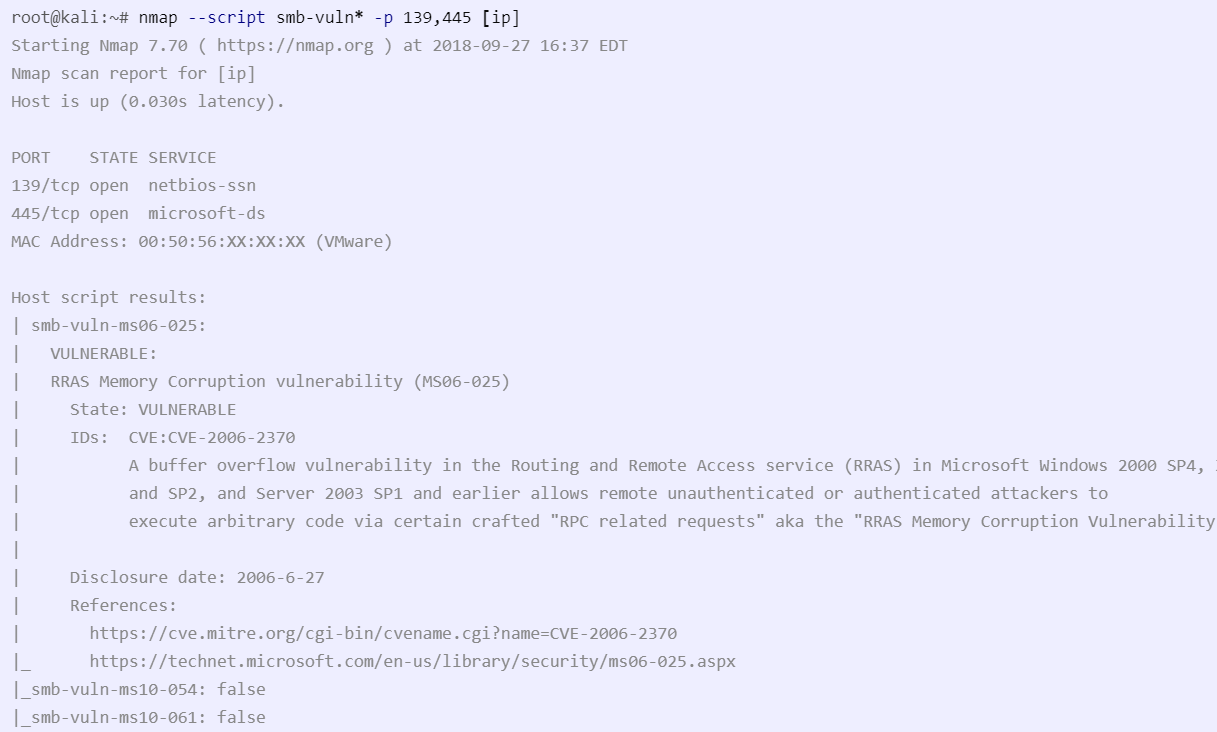
Overall Scan
enum4linux
enum4linux -a [ip]
-a- all enumeration
Example output is long, but some highlights to look for:
- output similar to nmblookup
- check for null session
- listing of shares
- domain info
- password policy
- RID cycling output
Manual Inspection
Samba
ngrep is a neat tool to grep on network data. Running something like ngrep -i -d tap0 's.?a.?m.?b.?a.*[[:digit:]]' port 139 in one terminal and then echo exit | smbclient -L [IP] in another will dump out a bunch of info including the version.
Script found on a PWK forum to easily get Samba versions:
#!/bin/sh
#Author: rewardone
#Description:
# Requires root or enough permissions to use tcpdump
# Will listen for the first 7 packets of a null login
# and grab the SMB Version
#Notes:
# Will sometimes not capture or will print multiple
# lines. May need to run a second time for success.
if [ -z $1 ]; then echo "Usage: ./smbver.sh RHOST {RPORT}" && exit; else rhost=$1; fi
if [ ! -z $2 ]; then rport=$2; else rport=139; fi
tcpdump -s0 -n -i tap0 src $rhost and port $rport -A -c 7 2>/dev/null | grep -i "samba\|s.a.m" | tr -d '.' | grep -oP 'UnixSamba.*[0-9a-z]' | tr -d '\n' & echo -n "$rhost: " &
echo "exit" | smbclient -L $rhost 1>/dev/null 2>/dev/null
sleep 0.5 && echo ""When you run this on a box running Samba, you get results:

When in doubt, we can check the smb version in PCAP. Here’s an example Unix Samba 2.2.3a:

Windows
Windows SMB is more complex than just a version, but looking in wireshark will give a bunch of information about the connection. We can filter on ntlmssp.ntlmv2_response to see NTLMv2 traffic, for example.
